In my last two posts OSPF Part-1 & Part-2 I have explained about Packet, State & LSA,s types. To continue our OSPF learning journey today will elaborate on Special areas.
OSPF SPECIAL
AREA TYPES:
There are four special areas in OSPF in the above picture.
First, let me
explain why we need a special area in OSPF. In our practical
live Network, there will be different types of Routers, switches & other
nodes, etc. Some with good performance like high CPU, Switching capacity, memory, etc., and other nodes will be not good in these parameters. In short, some will
store high numbers of routes & some few numbers of routes, to address this
problem different special areas are defined.
For example, if some routers are not good in performance
then make all routers in stub or totally stub area to limit the routes and
reduce routing table size.
Stub area:
Not allows LSA-5 & no ASBR allowed (LSA-4),
LSA1/2/3 are allowed.
Totally stub
area:
Not allow LSA
5 , No ASBR (LSA 4) & LSA 3.
In the stub area, inter-area routes are allowed & external
routes are not allowed but in totally stub area inter-area & external routes
both are not allowed. Now the question is then how they will communicate with
routes in other areas. The answer is through default routes. On ABR default
routes will be advertised to all nodes in that area.
In Not so
stubby area (NSSA) no LSA
5 & ASBR are allowed (LSA 4).
Totally NSSA,
No LSA 5 & LSA 3 but ASBR allowed (LSA 4).
The main
difference between Stub & NSSA terms is that in both stub areas, ASBR (LSA-4
not allowed) but in NSSA ASBR is allowed.
NSSA has its own ASBR in the area, let me explain the NSSA area
with the below example.
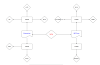
In the above topology, we have a total three areas 0,1 &
2. All areas are normal means no NSSA configuration.
Now let’s redistribute/import external routes on
Router-A in Area#2 and check the routing table of Router D & C in Area#1 , the
external routes 40.0.0.0 are learned and shown in the routing table.
The next step is to make Area-1 as NSSA (The NSSA
configuration I will show you later), Now again check the routing table of
Router D & C, this time no external route showing in table means that
External LSA-5 not allowed in the NSSA area same we studied above in NSSA
definition.
The focus point here is that the default route generated
on Route C in area-1 due to this we can communicate with an external Network.
Let me explain the other very important concepts in the same topology. As we studied in NSSA that ASBR (LSA-4) is allowed. This time import/redistribute external routes 50.0.0.0 on Router D of NSSA AREA#1 & check routing table & LSDB of same area routers C & D , external routes showing as NSSA LSA 7. Also, check on other area routers there it's showing as normal External Routes LSA-5.
Here is the key point that on ABR (Router-C) of NSSA area converts this LSA 7 to LSA 5 to advertise to other AREA#0. In this case optional bit (Propagate bit is used) that will be covered in the next post.
The summary of the NSSA area is that it has its own ASBR means we can import the external routes directly in the NSSA area but in the Stub area.
Configurations step & requirement:
Note the following points regarding the configuration of the Stub & NSSA area.
- ·
We cannot configure Backbone area#0
as a stub & NSSA Area.
- ·
For the indirectly connected area
with Backbone the virtual connection cannot pass through Stub & NSSA Area.
- ·
For the configuration of NSSA & Stub, we Need to configure on all routers in that area.
Below are the configuration examples on Cisco &
Huawei Devices.
Cisco Stub
Area:
(config)#router ospf 1
(config-router)#area 1 stub
Huawei Stub Area: #Ospf 1 #area 1 #stub
In OSPF part 1 & 2 I have explained about ospf packet types, states & explained all 11 LSAs.
Below is the link for your reference.
Link-1: https://www.readteknology.com/2024/01/ospf-interview-questions-answer-part-1.html
Link-2: https://www.readteknology.com/2024/01/ospf-interview-questions-answer-part-2.html
In Next post I will elaborate about Network Types, Optional Bits, and Topology & Header with advance
features of OSPF.





0 Comments