In a series of articles from Basic to advance Network Security, as today we will explain the topics Below.
- · NAT & its types
- · U-Turn NAT.
What is NAT?
NAT means translation of IP Address.
Normally everyone understands that translation from private (non-routable) to
public routable IP, but actually this translation can be between Private-to-Public
and Public-to-Private IP Addresses. Let’s Clarify in Details Below.
Types of NAT?
- Ø Source NAT
- Ø Destination NAT
Source NAT: In the source NAT below are two conditions
- Ø Traffic flow from LAN(Internal) to Internet
(WAN) and the source private IP address will be translated.
Types of Source
NAT:
Dynamic IP and Port
(DIPP) OR NAPT (Network Address port translation):
In this type of Source NAT, the Translation
of one-to-many IP Addresses plus different port number, for example in LAN have
10 hosts all are translating to one public IP Address with different port.
This NAT is also called interface-based
NAT as all Internal LAN hosts translate to one external Public IP Address.
Dynamic IP: Dynamic
translation of one-to-one means if five hosts in LAN & five public IP
Addresses then all are translating to unique public IP Addresses without
changing port number. If add one new host in LAN as now 6 then this host will
not translate & connection dropped.
The Best Design in this case is to
configure Dynamic IP & DIPP NAT.
Static NAT:
Static one-to-one translation means
manually assigning a public IP Address to a Private IP Address.
Static Vs Dynamic IP NAT:
The difference between static &
Dynamic IP is in the static fixed bond between private & public But in
Dynamic it’s randomly assigns one Public IP from out of multiple IP addresses.
Destination NAT:
Below are two conditions for destination NAT.
- Ø Traffic flow from the Internet (WAN) to LAN
(Internal Network) and Destination IP Address will be translated.in other words
translation of Public Destination IP Address to Private Destination IP Address.
Destination NAT is used in case when
Servers located in DMZ Zone that are accessing users from Public Internet means
Incoming Traffic.
Types of Destination
NAT:
Static NAT:
One-to-one Translation but it’s not
means that only one public destination IP Address translate to Private
Destination IP Address, In static NAT there will one-to-one or many-to-many
like range of IP Addresses.
Port translation & port forwarding
also possible in Destination NAT.
In Static DNAT we can configure port
forwarding & port translation as well.
Port forwarding means if server in DMZ
is listening on port 80 then if any request is received from outside internet
on port 80 HTTP default port number, then it’s just forward & fetch data.
But if the Server in DMZ is configured on port 8080 due to some security reason
default port is changed for HTTP services, for this need to configure Static
DNAT with port translation.
In Static DNAT two types.
- · Static DNAT with port forwarding
- · Static DNAT with port translation.
Dynamic IP (with
session distribution) NAT:
In this NAT translation or mapping of the
original (external interface IP or another IP of firewall) to Dynamic
Destination IP Address (Destination server IP address), means the destination IP
address is not static its changes from time to time.
If the original destination is one IP
Address in the packet from the internet (outside) needs to translate to
multiple destination IP Addresses (internal servers) means one outside IP map
to multiple inside IP Addresses then the firewall uses session distribution
against each translated IP address.
As the General & Original Packet options
are the same But in Dynamic IP NAT only Translated Packet portion change Below screenshot for reference & the most important thing here we can configure Dynamic IP/Port fallback
as well to achieve both DIPP & Dynamic IP functions.
Destination
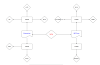
U-Turn NAT:
If some servers are running in DMZ
Zone & user are accessing from internet for required services. Now one user
in LAN same organization want to access these services for this no special
policy between LAN & DMZ but it’s through U-Turn NAT first go outside then
come back through internet to DMZ red arrow showing flow.
Below scenario of U-Turn NAT
In this type of NAT, both Source DIPP NAT & Static Destination need to configure. The source & Destination IP of the packet will be translated.
In Next section will cover other security-related
topics theoretically & with LAB implementation as well.
Keep Learning, Keep Reading,
and Keep Growing. IT & IP is the future.
Interview Questions:
- · What is NAT?
- · NAT Types?
- · Source & Destination NAT
- · U turn NAT
- · Static Vs Dynamic IP NAT
- · DIPP vs NAPT












0 Comments